Tuesday, February 12, 2008
JAMA: Effectiveness and Efficiency of Root Cause Analysis in Medicine
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
Effectiveness and Efficiency of Root Cause Analysis in Medicine
"Not all actions aimed to mitigate risk are equal. Some actions, like redesigning a product or process, are strong and have a high probability of reducing harm. Other actions, like reeducation or writing a policy, the 2 most common recommendations in health care RCA, are weak and have a low probability of reducing risk."
(Via JAMA current issue.)
Saturday, December 1, 2007
Anesthesiology: Predictors of Postoperative Acute Renal Failure
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
Predictors of Postoperative Acute Renal Failure after Noncardiac Surgery in Patients with Previously Normal Renal Function
"Background: The authors investigated the incidence and risk factors for postoperative acute renal failure after major noncardiac surgery among patients with previously normal renal function.
Methods: Adult patients undergoing major noncardiac surgery with a preoperative calculated creatinine clearance of 80 ml/min or greater were included in a prospective, observational study at a single tertiary care university hospital. Patients were followed for the development of acute renal failure (defined as a calculated creatinine clearance of 50 ml/min or less) within the first 7 postoperative days. Patient preoperative characteristics and intraoperative anesthetic management were evaluated for associations with acute renal failure. Thirty-day, 60-day, and 1-yr all-cause mortality was also evaluated.
Results: A total of 65,043 cases between 2003 and 2006 were reviewed. Of these, 15,102 patients met the inclusion criteria; 121 patients developed acute renal failure (0.8%), and 14 required renal replacement therapy (0.1%). Seven independent preoperative predictors were identified (P < 0.05): age, emergent surgery, liver disease, body mass index, high-risk surgery, peripheral vascular occlusive disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease necessitating chronic bronchodilator therapy. Several intraoperative management variables were independent predictors of acute renal failure: total vasopressor dose administered, use of a vasopressor infusion, and diuretic administration. Acute renal failure was associated with increased 30-day, 60-day, and 1-yr all-cause mortality.
Conclusions: Several preoperative predictors previously reported to be associated with acute renal failure after cardiac surgery were also found to be associated with acute renal failure after noncardiac surgery. The use of vasopressor and diuretics is also associated with acute renal failure."
Wednesday, July 4, 2007
Dark Chocolate Proven Healthy, Again
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
JAMA: Effects of Low Habitual Cocoa Intake on Blood Pressure and Bioactive Nitric Oxide
"Results: From baseline to 18 weeks, dark chocolate intake reduced mean (SD) systolic BP by –2.9 (1.6) mm Hg (P < .001) and diastolic BP by –1.9 (1.0) mm Hg (P < .001) without changes in body weight, plasma levels of lipids, glucose, and 8-isoprostane. Hypertension prevalence declined from 86% to 68%. The BP decrease was accompanied by a sustained increase of S-nitrosoglutathione by 0.23 (0.12) nmol/L (P < .001), and a dark chocolate dose resulted in the appearance of cocoa phenols in plasma. White chocolate intake caused no changes in BP or plasma biomarkers.
Conclusions: Data in this relatively small sample of otherwise healthy individuals with above-optimal BP indicate that inclusion of small amounts of polyphenol-rich dark chocolate as part of a usual diet efficiently reduced BP and improved formation of vasodilative nitric oxide."
With a change of roughly 3 systolic points and 2 diastolic points I'm not going to stop taking my Prinivil just yet.....
Thursday, June 21, 2007
Viagra for Bone Cement Impaction Syndrome?
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
In sheep, the phosphodiesterase inhibitor sildenafil (Viagra) prevents the catastrophic changes in pulmonary artery pressure that fat embolism can cause:
Sildenafil Prevents Cardiovascular Changes after Bone Marrow Fat Embolization in Sheep.
Saturday, May 19, 2007
"Not All Hyperglycemia is the Same"
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
One of my almost daily frustrations is the imprecise description of what kind of diabetes patients have. I'm often told, or see written, that a patient has 'insulin dependent diabetes' just because they are taking insulin. Dr. RW points to the second in a series of articles on diabetes in the journal Clinical Diabetes. It's a good review for me that I may use as the basis for a 'refresher' for the nurses...
[Dr. RW]
Monday, April 2, 2007
Do Specialty Hospitals Call 911 to Save Their Patients, or Transport Them?
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
The New York Times has an article titled Some Hospitals Call 911 to Save Their Patients which details two cases of patients having surgery at a specialty surgical hospital, experiencing complications, and then being transferred to a medical center (where they ultimately died). The whole article is written, and certainly the title was chosen, to suggest that 911 emergency services were called in order to treat a deteriorating patient as no physicians routinely stay in-house overnight.
Although I am not familiar with the particulars of the two cases mentioned in the New York Times article, it should be known that 911 would be called for any intra-facility transfer and does not necessarily imply they were called to render care in an emergency or that care was unavailable from other professionals already there.
Isn't it interesting, though, that a patient who is has no objection to getting their care from a CRNA, nurse practitioner, physician's assistant, or other 'health care provider' (after all, it's cheaper, right?) suddenly deems it essential to have a doctor there when things start to go south? Of course they do. I would, too!
If you're flying a commercial flight and the landing gear won't deploy, you feel better knowing the pilot is a former military pilot with years of experience in 'heavies.' If your child's safety is threatened by a stranger, you feel better knowing that highly trained and qualified officers are there to protect you. If you're having surgery and things start to go bad, you want an anesthesiologist, a physician, a smart, independent thinker who doesn't get flustered or do whatever the surgeon says to do. You want me. Not someone who is cheaper, less highly trained, less experienced, someone who will do in 99% of cases.
Monday, March 12, 2007
CDC: Quadrivalent Human Papillomavirus Vaccine
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP)
"Routine Vaccination of Females Aged 11--12 Years
ACIP recommends routine vaccination of females aged 11--12 years with 3 doses of quadrivalent HPV vaccine. The vaccination series can be started as young as age 9 years.
Catch-Up Vaccination of Females Aged 13--26 Years
Vaccination also is recommended for females aged 13--26 years who have not been previously vaccinated or who have not completed the full series. Ideally, vaccine should be administered before potential exposure to HPV through sexual contact; however, females who might have already been exposed to HPV should be vaccinated. Sexually active females who have not been infected with any of the HPV vaccine types would receive full benefit from vaccination. Vaccination would provide less benefit to females if they have already been infected with one or more of the four vaccine HPV types. However, it is not possible for a clinician to assess the extent to which sexually active persons would benefit from vaccination, and the risk for HPV infection might continue as long as persons are sexually active. Pap testing and screening for HPV DNA or HPV antibody are not needed before vaccination at any age. "
Thursday, March 8, 2007
Why Are C-Section Rates Still Going Up?
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
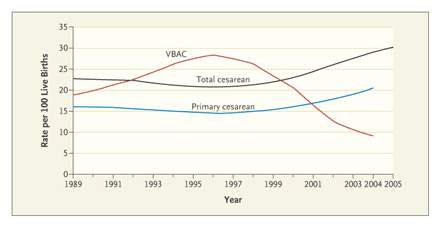
As an anesthesiologist I provide anesthesia for cesarean sections quite often. In fact, when I'm on overnight call it's what I spend most of my time doing. Usually, anesthesia for c-section consists of a spinal anesthetic, or using a pre-existing epidural catheter, or (more rarely and usually only in emergencies) a general anesthetic. I am therefore quite interested in the subject of cesarean section rates and what effects how often they are done. I learned some things from this article [free full text]:
Cesarean Delivery and The Risk-Benefit Calculus
1. Parturients are different--they are heavier and older.
2. The number of premature and low birth-weight babies has grown.
3. Vaginal breech deliveries are no longer recommended.
4. Operative deliveries (forceps or vacuum) are less common due to better data describing their risks.
5. More labors are induced (20% in 2003 vs 9.5% in 1990) and induced labors are more likely to result in C-section.
6. Changes in provider behavior
"At least one study found that physicians' malpractice premiums, the number of claims against physicians and hospitals, and the physician's preception of the risk fo being sued were all positively correlated with the likelihood of cesarean delivery. Many in the field defend the rising cesarean rates by citing concern about legal jeopardy, and indeed lawsuits often allege a failure to perform a timely cesarean delivery."
Look at John Edwards' list of law cases (thank you, Google). Notice the medical malpractice cases:
MEDICAL MALPRACTICE CASES
Another specialty Edwards developed was in medical malpractice cases involving problems during births of babies. According to the New York Times, after Edwards won a $6.5M verdict for a baby born with cerbral-palsy, he filed at least 20 similar lawsuits against doctors and hospitals in deliveries gone wrong, winning verdicts and settlements of more than $60M.
|
| Case |
Summary of Facts |
Case Type |
Result |
Griffin v. Teague, et al.
(Mecklenburg Co. Superior Ct., NC, 1997) |
Application of abdominal pressure and delay in performing c-section caused brain damage to infant and resulted in child having cerebral palsy and spastic quadriplegia. Verdict set record for malpractice award. |
Medical Malpractice |
$23.25M
verdict |
Campbell v. Pitt County Memorial Hosp.
(Pitt County, NC, 1985)
|
Infant born with cerebral palsy after breech birth via vaginal delivery, rather than cesarean. Established North Carolina precedent of physician and hospital liability for failing to determine if patient understood risks of particular procedure. |
Medical
Malpractice |
$5.75M
settlement |
| Wiggs v. Glover, et al. |
Plaintiff alleged infant's severe cerebral palsy was caused by negligent administration of pitocin, failure to use fetal monitor, or timely intervening in baby's fetal distress. |
Medical
Malpractice |
2.5M
settlement |
| Cooper v. Craven Regional Med. Ctr., et al. |
Infant suffered severe brain damage after obstetrician failed to moderate use of Picotin after baby displayed clear fetal distress. |
Medical
Malpractice |
$2.5M
settlement |
Dixon v. Pitt County Memorial Hospital
(Pitt County, NC) |
Birth-related injuries including cerebral palsy and mental retardation allegedly caused by obstetrician's failure to diagnose fetal distress, including umbilical cord wrapped around baby's neck prior to delivery. |
Medical
Malpractice |
2.4M
settlement
|
Despite the increase in c-section rates nationwide, we have seen no reduction in the cerebral palsy rate...
Details On Why We Get Migraines
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
"A University of Iowa study may provide an explanation for why some people get migraine headaches while others do not. The researchers found that too much of a small protein called RAMP1 appears to "turn up the volume" of a nerve cell receptor's response to a neuropeptide thought to cause migraines.
"The neuropeptide is called CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) and studies have shown that it plays a key role in migraine headaches. In particular, CGRP levels are elevated in the blood during migraine, and drugs that either reduce the levels of CGRP or block its action significantly reduce the pain of migraine headaches. Also, if CGRP is injected into people who are susceptible to migraines, they get a severe headache or a full migraine.
"We have shown that this RAMP protein is a key regulator for the action of CGRP," said Andrew Russo, Ph.D., UI professor of molecular physiology and biophysics. "Our study suggests that people who get migraines may have higher levels of RAMP1 than people who don't get migraines." "
The abstract is here.
Wednesday, March 7, 2007
Aspirin/NSAIDs For Colorectal Cancer Prevention Discouraged
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
"People who are at average risk for colorectal cancer, including those with a family history of the disease, should not take aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to try to prevent the disease, according to a new recommendation from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. The recommendation is published in the March 6 issue of the Annals of Internal Medicine."
"USPSTF assessment: Overall, the USPSTF concluded that harms outweigh the benefits of aspirin and NSAID use for the prevention of colorectal cancer."
[AHRQ]
AFP: Preparation of the Cardiac Patient for Noncardiac Surgery
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
Excellent Lee Fleisher article in American Family Physician [free full text] for any primary care physician who is asked to do pre-op medical evaluations (note I didn't use the word 'clearance').
Tuesday, February 27, 2007
JAMA: Prevalence of HPV Infection Among Females in the United States
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
Prevalence of HPV Infection Among Females in the United States [free full text]
"Our study provides the first national estimate of prevalent HPV infection among females aged 14 to 59 years in the United States. Overall, HPV prevalence was high (26.8%), and prevalence was highest among females aged 20 to 24 years [ed. where it was 44%]. Our data indicate that the burden of prevalent HPV infection among women was higher than previous estimates. However, the prevalence of HPV vaccine types was relatively low."
Remember, prevalence is the proportion of cases that are present at a single point in time.
For a background primer on HPV infection, see the excellent JAMA Patient Page.
| |
1 |
2 |
| 3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
| 10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
| 17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
| 24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
|
|
Dec Mar
|

![]()