Wednesday, May 24, 2006
If it's not one virus, it's another
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
Bird flu has been very much in the news, but now another type of virus is also threatening: chikungunya virus (named with a Swahili word meaning 'bent up').
"The chikungunya virus has infected around one-third of the population (about 250,000 people) on the French island of Réunion since early 2005. It has also hit the neighbouring islands of Mauritius, Seychelles, Madagascar and Mayotte, and reared its head in India."
With only a little over 200 deaths it's not near as big a killer as H5N1 might be, but it would wreak havoc nonetheless. Fevers over 102 and arthralgias. Yuck.
Tuesday, February 28, 2006
Bird Flu Now Cat Flu....in Germany
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
Bird Flu Found in Cat in Germany after eating infected bird.
Sunday, January 29, 2006
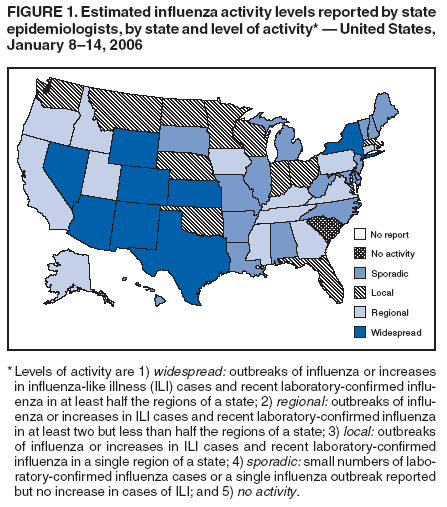
Influenza Map--through Jan. 14, 2006
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
Thursday, December 22, 2005
Another report of H5N1 resistance to Tamiflu
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
NEJM Case Report: Oseltamivir Resistance during Treatment of Influenza A (H5N1) Infection [free full text]
Thursday, November 24, 2005
NEJM: The Origins of Pandemic Influenza--Lessons from the 1918 Virus
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
The Origins of Pandemic Influenza--Lessons from the 1918 Virus [free full text]
"...monitoring of the sequences of viruses isolated in instances of bird-to-human transmission for genetic changes in key regions may enable us to track viruses years before they develop the capacity to replicate with high efficiency in humans. Knowledge of the genetic sequences of influenza viruses that predate the 1918 pandemic would be extremely helpful in determining the events that may lead to the adaptation of avian viruses to humans before the occurrence of pandemic influenza. We could then conduct worldwide surveillance for similar events involving contemporary avian viruses. "
Saturday, October 15, 2005
Bird flu virus reported to resist Tamiflu
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
More popular press stories on drug resistance in bird flu:
"An avian influenza virus isolated from an infected Vietnamese girl has been determined to be resistant to the drug oseltamivir, the compound better known by its trade name Tamiflu, and the drug officials hope will serve as the front line of defense for a feared influenza pandemic. [Science Blog - Science News Stories]"
The New England Journal of Medicine has a recent free article summarizing our current state of knowledge titled Avian Influenza A (H5N1) Infection in Humans:
"High-level antiviral resistance to oseltamivir results from the substitution of a single amino acid in N1 neuraminidase (His274Tyr). Such variants have been detected in up to 16 percent of children with human influenza A (H1N1) who have received oseltamivir. Not surprisingly, this resistant variant has been detected recently in several patients with influenza A (H5N1) who were treated with oseltamivir."
This is not to say, however, that we have no other neuraminidase inhibitor tricks up our sleeves.
Monday, March 14, 2005
WHO warns of human bird flu mutation
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
ABC News Online--WHO warns of human bird flu mutation.:
" The World Health Organisation (WHO) says the bird flu virus may be changing into a form that humans can pass on.
The WHO is worried that bird flu, which has killed 47 people in Asia, could mutate into an easily spread form that sparks the next influenza pandemic.
The organisation has identified a cluster of human bird flu cases among relatives and possibly health workers in Vietnam.
"Such cases can provide the first signal that the virus is altering its behaviour in human populations and thus alert authorities to the need to intervene quickly," the WHO said in a statement.
The main concern of the WHO was a series of cases of the deadly H5N1 bird flu virus in a family in the northern Vietnam province of Thai Binh and the possible infection of two nurses who cared for one of the patients.
The WHO also says it has received confirmation of an additional 10 cases of human infections from Vietnam's Health Ministry.
The new cases were detected in early March or through re-examination of older cases, some of which dated back to late January and three of which had been fatal, the WHO said. "
See the WHO web site for details.
Wednesday, February 16, 2005
New Manifestations of Avian Influenza A (H5N1)
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
NEJM--Fatal Avian Influenza A (H5N1) in a Child Presenting with Diarrhea Followed by Coma:
" In southern Vietnam, a four-year-old boy presented with severe diarrhea, followed by seizures, coma, and death. The cerebrospinal fluid contained 1 white cell per cubic millimeter, normal glucose levels, and increased levels of protein (0.81 g per liter). The diagnosis of avian influenza A (H5N1) was established by isolation of the virus from cerebrospinal fluid, fecal, throat, and serum specimens. The patient's nine-year-old sister had died from a similar syndrome two weeks earlier. In both siblings, the clinical diagnosis was acute encephalitis. Neither patient had respiratory symptoms at presentation. These cases suggest that the spectrum of influenza H5N1 is wider than previously thought. "
Thursday, December 9, 2004
NEJM -- The Genetic Archaeology of Influenza
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
NEJM -- The Genetic Archaeology of Influenza:
" "Different strains of influenzavirus have different pathologic effects. For example, infection by the so-called Spanish influenzavirus caused more than 20 million deaths in 1918 and 1919, many of which were due to hemorrhagic pneumonia. To identify the critical components of this virus, mouse-adapted influenza A viruses (Panel A) were modified by Kobasa et al. so that these viruses expressed the form of hemagglutinin encoded by the gene of the 1918 Spanish influenza strain (HAsp), alone (Panel C) or in combination (Panel B) with the form of neuraminidase encoded by the gene of the 1918 Spanish influenza strain (NAsp). They concluded that the HAsp protein is critical to the enhanced cytokine production, inflammation, and hemorrhagic pneumonia that characterized this virulent influenza." "
![]()
" "This new study has important clinical and epidemiologic implications. Assuming that the mouse model at least partially reflects the important factors in the virulence of influenza in humans, further dissection of the HAsp molecule is warranted to help identify the critical structural motifs that confer enhanced virulence. This can be accomplished by performing site-directed mutational analyses of the HAsp gene and investigating the effects of these mutations on infection in the mouse model. The identification of these motifs may provide a new epidemiologic tool for surveillance of circulating animal and human influenzaviruses that could be used to predict the emergence of a new, highly virulent pandemic strain. In addition, these detailed molecular studies could facilitate the identification of antigenic epitopes to include in vaccines in order to protect people against related pandemic strains." "
The above comments are in reference to a recent article in Nature titled Enhanced virulence of influenza A viruses with the haemagglutinin of the 1918 pandemic virus. This is exciting and excellent work which opens the way for more fundamental basic science animal research as well as clinical studies.
Friday, December 3, 2004
Pennsylvania Has Its First Influenza Case
-
Printer Friendly|#| Trackback
Type A-Fujian influenza has been confirmed in a Philadelphia resident, the first laboratory-confirmed case of influenza in Pennsylvania. Of note, this strain was included in the vaccine.
| |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
| 7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
| 14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
| 21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
| 28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
|
|
Feb Nov
|
